Thyroid in Kids: Everything You Need to Know
The thyroid gland plays a crucial role in the overall health and development of children. As a butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, the thyroid produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and energy levels. Understanding thyroid health in children is essential for parents and caregivers. Here’s everything you need to know.
1. What is the Thyroid Gland?
The thyroid gland produces two primary hormones: thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones are vital for many bodily functions, including:
- Metabolism: How the body converts food into energy.
- Growth and Development: Crucial during childhood and adolescence.
- Body Temperature Regulation: Helps maintain a stable body temperature.
2. Common Thyroid Disorders in Children
Children can experience various thyroid-related conditions, including:
-
Hypothyroidism: This condition occurs when the thyroid does not produce enough hormones. Symptoms may include fatigue, weight gain, sensitivity to cold, constipation, dry skin, and delayed growth.
-
Hyperthyroidism: In contrast, hyperthyroidism results from excessive hormone production. Symptoms can include rapid heartbeat, weight loss, increased appetite, nervousness, and sweating.
-
Congenital Hypothyroidism: This condition is present at birth and is usually detected through newborn screening. Early treatment is crucial for healthy growth and development.
3. Symptoms of Thyroid Issues
Parents should be aware of the signs that may indicate a thyroid problem in their child. Common symptoms include:
-
Hypothyroidism:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Weight gain despite a normal diet
- Cold intolerance
- Constipation
- Dry skin and hair
- Slow growth or delayed puberty
-
Hyperthyroidism:
- Unexplained weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Hyperactivity or nervousness
- Sweating and heat intolerance
- Rapid heart rate
4. Diagnosis and Screening
Thyroid issues in children can be diagnosed through:
- Blood Tests: Measuring levels of TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone), T3, and T4 can help determine thyroid function.
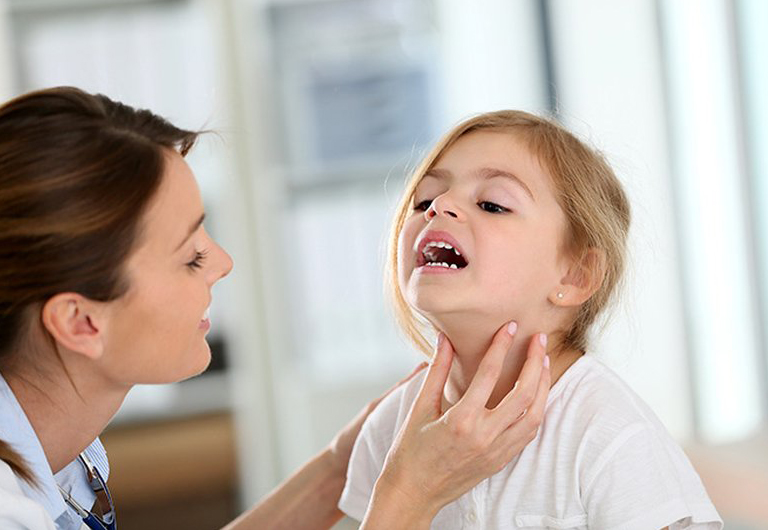
- Physical Exam: A healthcare provider may check for signs of thyroid dysfunction, such as goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland) or changes in growth patterns.
- Newborn Screening: Most states conduct routine newborn screenings to detect congenital hypothyroidism.
5. Treatment Options
Treatment for thyroid disorders depends on the specific condition:
-
Hypothyroidism: Typically managed with synthetic thyroid hormone replacement therapy (levothyroxine), which helps normalize hormone levels and supports growth and development.
-
Hyperthyroidism: Treatment options may include medications to reduce hormone production, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery in severe cases.
6. Importance of Monitoring
Regular check-ups and monitoring are essential for children with thyroid disorders. This ensures that hormone levels remain stable and that any changes in symptoms are promptly addressed. Pediatric endocrinologists are specialists who can provide comprehensive care for children with thyroid issues.
7. Nutritional Considerations
Nutrition plays a vital role in thyroid health. Encourage a balanced diet that includes:
- Iodine: Essential for hormone production. Sources include iodized salt, fish, dairy, and eggs.
- Selenium: Supports thyroid function and can be found in nuts, seeds, and fish.
- Zinc: Important for hormone regulation, present in meats, beans, and whole grains.
Conclusion
Understanding the role of the thyroid in children is crucial for early detection and effective management of thyroid disorders. If you notice any concerning symptoms or have questions about your child’s thyroid health, consult a healthcare professional for guidance and support.